
How to Configure Magento 2.4 with Docker
The Docker platform offers flexibility and scaling for Magento 2 stores.
You can manage multiple applications in the Docker container. It improves application development and security with cross-process isolation.
You can also use a local development environment such as MGT Development Environment. It is completely based on Docker to ease Magento application development.
The tutorial shows the steps to install and configure Magento 2.4 using Docker.
Steps to Install and Configure Magento 2.4 with Docker
Magento 2.4 Docker Setup Blueprint
Your 12-step journey from project creation to production-ready e-commerce
Initial Setup & Configuration
Create Project with Composer
Initialize Magento 2.4 project with version selection
Navigate to Project Root
Enter the newly created project directory
Download Cloud Docker Tools
Add Magento Cloud Docker package for containerization
Add Docker Configuration
Create .magento.docker.yml with service definitions
Copy Configuration to Root
Move Docker config to project root directory
Add .magento.app.yaml
Configure application settings and hooks
Install Composer Dependencies
Download all required packages and libraries
Add auth.json Credentials
CRITICALConfigure Magento Marketplace authentication for package access
Container Deployment
Build Container Files
Generate Docker configuration and build images
Deploy Magento Container
Launch Docker containers and initialize services
Final Configuration
Configure Varnish Cache
Set up enterprise-level caching for performance
Clear Cache & Launch
COMPLETEFinal cache clearing and production access
Critical Docker Services
Default Admin Credentials
1. Create a project using Composer.
We first create a directory to setup Magento 2 and run the following code below-
composer create-project --repository-url=https://repo.magento.com/ magento/project-community-edition <install-directory-name>
The install command is shown above will install the latest Magento release.
To install a specific Magento version, enter the version number.
For example -
magento/project-community-edition=2.4.2
2. Change to the Project directory
For <install-directory-name> you may have given a name such as example.com.
Switch to the project directory in the server to run the next set of commands.
cd <install-directory-name>
3. Add the ece-tools and Cloud Docker
Using the following command, add the ece-tools and cloud docker for community packages.
Cloud Docker let you to deploy Magento 2.4 to a Docker environment. It can be used for development, testing, and automation tasks.
composer require --no-update --dev magento/ece-tools magento/magento-cloud-docker
4. Create a default configuration source file
The Magento 2.4 Stack Decoded
Your 4-Service Architecture Blueprint - Tested versions that work together seamlessly
Persistent Mount Points
var
Variable Data
app/etc
Configuration
pub/media
Media Files
pub/static
Static Assets
Deployment Mode: PRODUCTION
Optimized for performance over development convenience
Now we create the default configuration source file .magento.docker.yml
It is used to build the Docker containers for the local environment.
The configuration for Magento version 2.4.2 is shown below -
system:
mode: 'production'
services:
php:
version: '7.4'
extensions:
enabled:
- xsl
- json
- redis
mysql:
version: '10.4'
image: 'mariadb'
redis:
version: '6.0'
image: 'redis'
elasticsearch:
version: '7.9.0'
image: 'magento/magento-cloud-docker-elasticsearch'
hooks:
build: |
set -e
php ./vendor/bin/ece-tools run scenario/build/generate.xml
php ./vendor/bin/ece-tools run scenario/build/transfer.xml
deploy: 'php ./vendor/bin/ece-tools run scenario/deploy.xml'
post_deploy: 'php ./vendor/bin/ece-tools run scenario/post-deploy.xml'
mounts:
var:
path: 'var'
app-etc:
path: 'app/etc'
pub-media:
path: 'pub/media'
pub-static:
path: 'pub/static'
You can also config suitable services for different Magento versions. Check out the system requirements for more information.
The software dependencies are tested for specific Magento versions. Use the table for your preferred Magento versions.
5. Use the Magento Installation Script
The installation script will add the template dependencies. It will also install the default hostname to your /etc/hosts file.
curl -sL https://github.com/magento/magento-cloud-docker/releases/download/1.2.3/init-docker.sh | bash -s -- --php 7.4
6. Update the project dependencies
You can update the project dependencies with the following command.
composer update
7. Generate the Docker Compose Configuration file
./vendor/bin/ece-docker build:compose --mode="developer"
After this script is complete, you will see the file name docker-compose.yml.
The file is the Docker Compose configuration file.
In some cases, the image for docker is generated incorrectly. You have to edit the file and correct it according to the Magento version.
Also, correct the image Tags version in the Magento Docker hub.
8. Add auth.json file
Log in to the Magento Marketplace > go to My Profile > select Access Keys or Create a New Access Key if required.
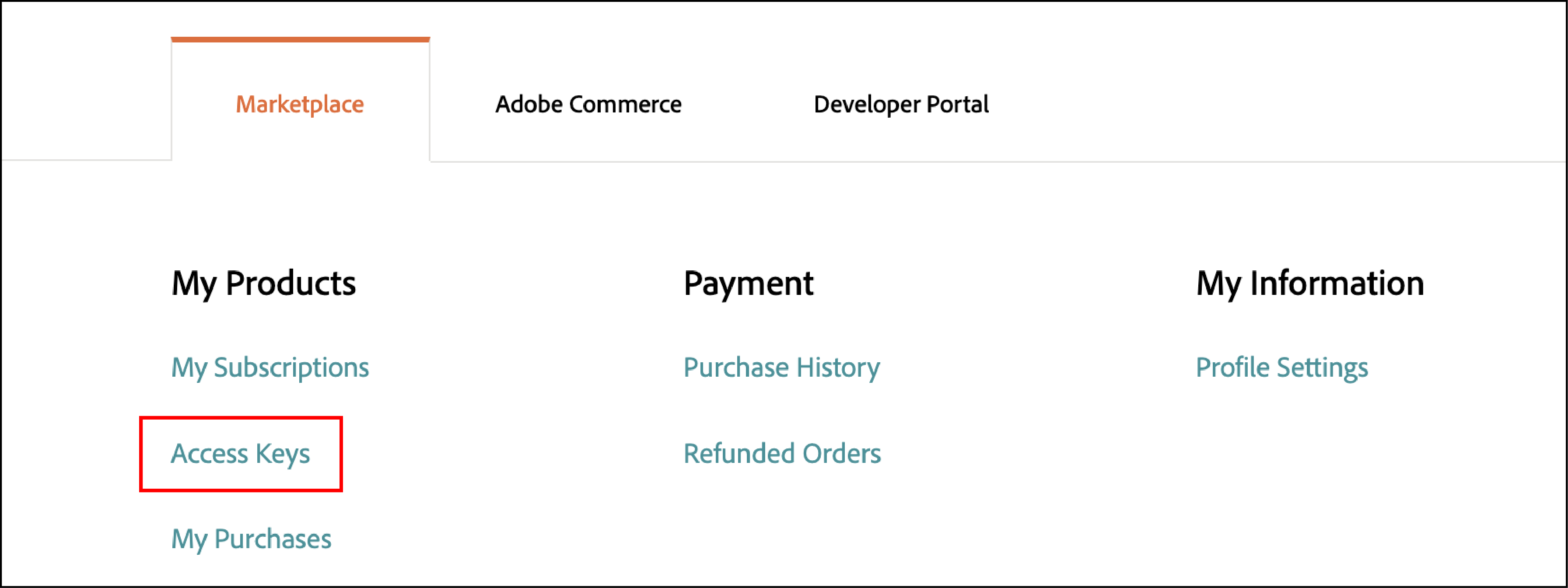
The <public-key> and <private-key> should be available from the panel.
Create a file name auth.json which contains the below content in your project directory.
{
"http-basic": {
"repo.magento.com": {
"username": "<public-key>",
"password": "<private-key>"
}
}
}
9. Build files to the container.
Use the following command to build files to the container and run in the background.
docker-compose up -d
10. Deploy Magento is a Docker container
From Container to Commerce: The 3-Phase Magento Deployment Journey
Follow the deployment timeline to see how each command transforms your containers
cloud-deploy
Handles core Magento installation and database setup
docker-compose run --rm deploy cloud-deploy
developer mode
Switches from production for debugging capabilities
deploy:mode:set developer
cloud-post-deploy
Finalizes configurations and runs optimization scripts
docker-compose run --rm deploy cloud-post-deploy
Varnish Configuration
Full-page cache setup reducing server load by 80-90%
config:set system/full_page_cache/caching_application 2
Step 11: Enable Varnish cache
setup:config:set --http-cache-hosts=varnish
Connect to Varnish service
docker-compose run --rm deploy magento-command cache:clean
Step 12: Clear cache for testing
docker-compose run --rm deploy cloud-deploy
docker-compose run --rm deploy magento-command deploy:mode:set developer
docker-compose run --rm deploy cloud-post-deploy
11. Configure and Connect Varnish
The next step is setting up varnish and connecting with Magento.
docker-compose run --rm deploy magento-command config:set system/full_page_cache/caching_application 2 --lock-env
docker-compose run --rm deploy magento-command setup:config:set --http-cache-hosts=varnish
12. Clear the Cache
The final step is to clear the cache and check the results. Use the following command to clear the cache -
docker-compose run --rm deploy magento-command cache:clean
Access the local Magento Cloud template through http://magento2.docker or https://magento2.docker
Use the default credentials to log in to the Admin panel -
https://magento2.docker/admin
- Username = Admin
- Password = 123123q
We are now done installing Magento 2.4 on Docker and use it on a common operating system.
You can set up the entire technology stack for Magento in the Docker container and create the image.
The docker image is portable to create another container immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions
Docker vs Traditional: Why Modern Magento Development Has Evolved
Quantifiable advantages that transform development workflows
Docker-Based Setup
Traditional Setup
PHP Version Support
Concurrent versions
Security Layers
Isolation level
Setup Speed
Time to deploy
Environment Consistency
Cross-platform portability
Service Architecture
Component isolation
Setup Process
Configuration steps
Key Advantage
Docker transforms Magento development from hours of manual server configuration to minutes of automated container deployment, while providing superior isolation, portability, and the ability to run multiple PHP versions simultaneously.
What is magento2.docker and how is it used in Magento 2.4 installation?
Magento2.Docker is a default hostname used during the installation of Magento 2.4 with Docker. It allows you to access the local Magento Cloud template through http://magento2.docker or https://magento2.docker. It simplifies the setup process and provides a consistent environment for development and testing.
How does docker-magento help in Magento 2.4 installation and configuration?
Docker-Magento helps to simplify the process of setting up a Magento 2.4 development environment by creating Docker containers with all required configurations and services. It allows developers to run multiple PHP versions simultaneously, provides additional security layers, and makes it easy to manage and deploy Magento 2 applications.
Can you provide some Magento community examples of using Docker for Magento 2 installation?
Some Magento community examples of using Docker for Magento 2 installation include:
- The Magento Cloud Docker repository, which provides a Docker-based development environment for local Magento Cloud projects.
- The MGT Development Environment, which is based on Docker and helps developers build and ship PHP applications faster.
- Various Magento community members sharing their experiences and tutorials on using Docker for Magento 2 installation and development on blogs and forums.
How do I dockerize Magento 2 for easier development and deployment?
To dockerize Magento 2, follow these steps:
- Create a project using Composer.
- Change to the project directory.
- Add the ece-tools and Cloud Docker for community packages.
- Create a default configuration source file
.magento.docker.yml. - Use the Magento installation script to add template dependencies and set up the default hostname.
- Update the project dependencies using Composer.
- Generate the Docker Compose configuration file.
- Add an
auth.jsonfile with your Magento Marketplace access keys. - Build files to the container and run it in the background using
docker-compose up -d. - Deploy Magento in a Docker container by executing the required commands.
- Configure and connect Varnish.
- Clear the cache and access your Magento 2 instance through
http://magento2.dockerorhttps://magento2.docker.
By following these steps, you can create a portable Docker image with the entire technology stack for Magento 2 development and deployment.
EndNote
Docker container technology eases the process of developing Magento websites. It offers all-in-one packages for a suitable runtime environment. You can create separate instances for many purposes on a single underlying host machine.
The Docker containers can run multiple PHP versions at the same time. It also provides an additional security layer for accessing the website code.
To develop locally, check out the MGT Development Environment. It is based on Docker and allows you to build and ship PHP applications faster.
You can also go to the MGT-Commerce tutorials page for the latest Magento 2 information.



